Random Forest
Random Forest其实就是在Bagging的基础上添加随机属性,Bagging Tree就是基于Bootstrape训练多个Tree。下面将一一进行展开
Bagging Tree
Bagging Tree就是基于Bootstrape生成多个训练集,然后基于这些训练集得到多个CART,检测时使用这多个CART进行检测,即:
-
Bootstrape
假设有训练集有N个样本,则在这N个样本中随机挑训N个样本作为新的训练集(其可以有重复),如下:
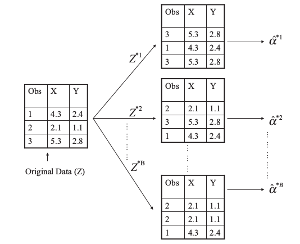
-
重点
- Bagging Tree的
每一个子树不需要Prune,其是通过平均多个子树来降低Variance的 - Bagging的缺点是
可能其每一个子树都比较相似,导致最终并不能带来很大的提高(Random Fores很好的解决了这个问题) - 实验表明,每次bootstrape生成的样本只占训练集的2/3。其他1/3的部分可以用来测试
- Bagging Tree的
Random Forest
Random Forest就是在Bagging tree的基础上增加了随机的属性。即在构建树时,每次用来进行分割的特征是随机选择的一个子集,而不是所有特征。因此就算完全一样的训练,其生成的树也是不同的。有效的解决了Bagging Tree中的子树相似的问题
Random Ferns
单个Fern的构建:假设有D为特征,则随机挑选S个特征,并在这S个特征上随机的挑选一个阈值进行分割。则最终有个leaf节点。Random Ferns即将多个Ferns结合在一起,详细见文章[2]
Boosting Tree
Boosting Tree用在回归上时,是不断的减少检测值与真实值之间的residual。分类时,其比较复杂,暂时不提供
- Regression
- Set f(x) = 0 and for all i in the training set.
- For b = 1, 2, . . . , B, repeat:
a). Fit a tree with d splits (d+1 leafs) to the training data(X, r)
b). Update f by adding in a shrunken version of the new tree:
c). Update the residuals:
(r为residual即真实值与预测值之间的差)- Output the boosted model:
- Classification
Coming soon
References
- An Introduction to Statistical Learning with Applications in R
- Fast keypoint recognition using random ferns